Introduction
Fiber optic color codes, fiber opitc, a cornerstone of modern communication technology, has revolutionized the way we transmit data. These slender, flexible fibers, made of glass or plastic, conduct light signals over long distances with astounding speed and reliability. An integral aspect of this technology is its color coding system. In fiber optics, color coding serves as a crucial visual guide for technicians and engineers. It simplifies cable identification, prevents errors in connectivity, and streamlines network setup. Adhering to color codes, especially in complex network environments, ensures efficiency and accuracy in installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Understanding Fiber Optic Cables
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are primarily classified into two types: singlemode and multimode fibers. Singlemode fibers, with their thinner core, are designed for long-distance communication, transmitting signals over several kilometers without significant loss. Conversely, multimode fibers have a wider core, allowing light signals to travel in multiple paths, ideal for shorter distances with high data transmission rates.

Role of Color Coding in Cable Identification
Color coding in fiber optics transcends mere aesthetics. It is a practical solution for differentiating various types of cables and their properties, like connector types (MPO, LC, SC), cable structures (ribbon cables, breakout cables, buffer tubes), and the fiber count within a cable. This color-coded system aligns with the TIA-598 Standards, ensuring consistency across the industry.
Color Codes in Fiber Optics
Standard Color Codes for Different Fiber Types
The industry follows a standardized color scheme to distinguish between singlemode and multimode fibers. Typically, yellow signifies singlemode fiber, while orange, aqua, and sometimes green represent multimode fibers. Each color not only indicates the fiber type but also provides clues about its performance characteristics and applications.

Explanation of TIA-598 Color Code Standards
The TIA-598 Standards provide a detailed framework for fiber optic color coding. This includes guidelines for internal fiber coding, cable jacket colors, and polarity maintenance. These standards are critical for maintaining consistency and safety in optical networks, including the setup of patch panels and splice trays.
Connector Color Codes
Color Coding for Fiber Optic Connectors
Connectors in fiber optic systems, such as LC, SC, and ST, follow a color-coded system. This coding helps in identifying the type of fiber connected and its corresponding performance characteristics. For example, a blue connector typically denotes a singlemode fiber, while beige or black indicates multimode.
Significance in Network Setups
In network setups, connector color codes play a pivotal role in ensuring correct and efficient connections. This is particularly vital in complex installations involving numerous connections, as it aids in quick identification and reduces the likelihood of errors during network setup and maintenance.
Cable Jacket Colors
Outer Jacket Color Significance
The color of a fiber optic cable’s jacket is more than just a visual identifier. It provides essential information about the cable’s usage and environmental suitability. For instance, different colors can indicate whether a cable is designed for indoor, outdoor, or plenum use.

Standards for Cable Jacket Colors
These jacket colors are standardized, often following the TIA-598 guidelines. Adhering to these standards ensures that cables are used appropriately and safely in their intended environments.
Fiber Color Codes
Internal Fiber Color Coding
Inside a fiber optic cable, each individual fiber is color-coded for easy identification. This internal coding is crucial for maintaining proper sequence and polarity, especially during splicing and installations involving multiple fibers.
Guidelines for Splicing and Continuity
Following the correct color sequence is essential for maintaining signal continuity and ensuring efficient network performance. The color codes serve as a guide for technicians during the splicing process, ensuring that fibers are aligned correctly in splice trays and patch panels.
FAQs Section

What is the color code for fiber optic?
The color code for fiber optic cables varies based on the type of fiber and its application. Generally, yellow is used for singlemode fibers, while orange, aqua, and green are used for multimode fibers.
How do I remember my fiber optic color code?
Remembering fiber optic color codes can be aided by mnemonic devices or charts that correlate colors with fiber types and applications.
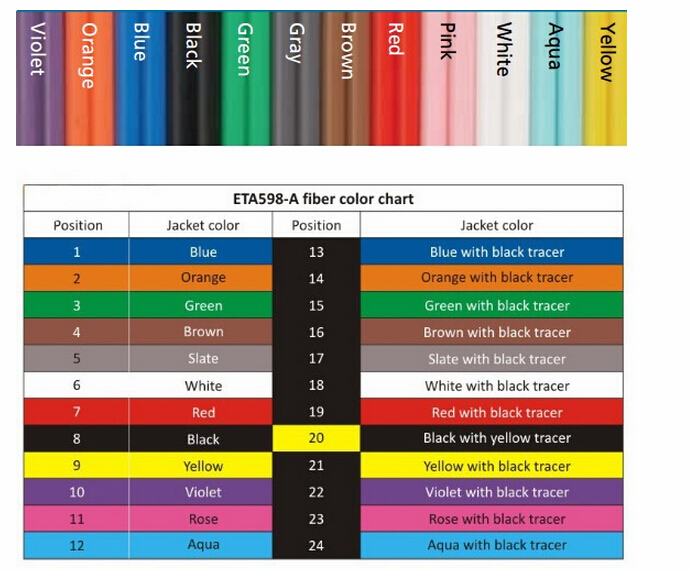
What are the 12 core colors of optical fiber?
The 12 core colors in a standard fiber optic cable are blue, orange, green, brown, slate, white, red, black, yellow, violet, rose, and aqua.
What is the color order of fiber?
The standard color order for fiber coding starts with blue, followed by orange, green, brown, slate, white, red, black, yellow, violet, rose, and aqua.